Determination of the Henry constant for the dissolution of CO2 in a diet coke
Main Article Content
Abstract
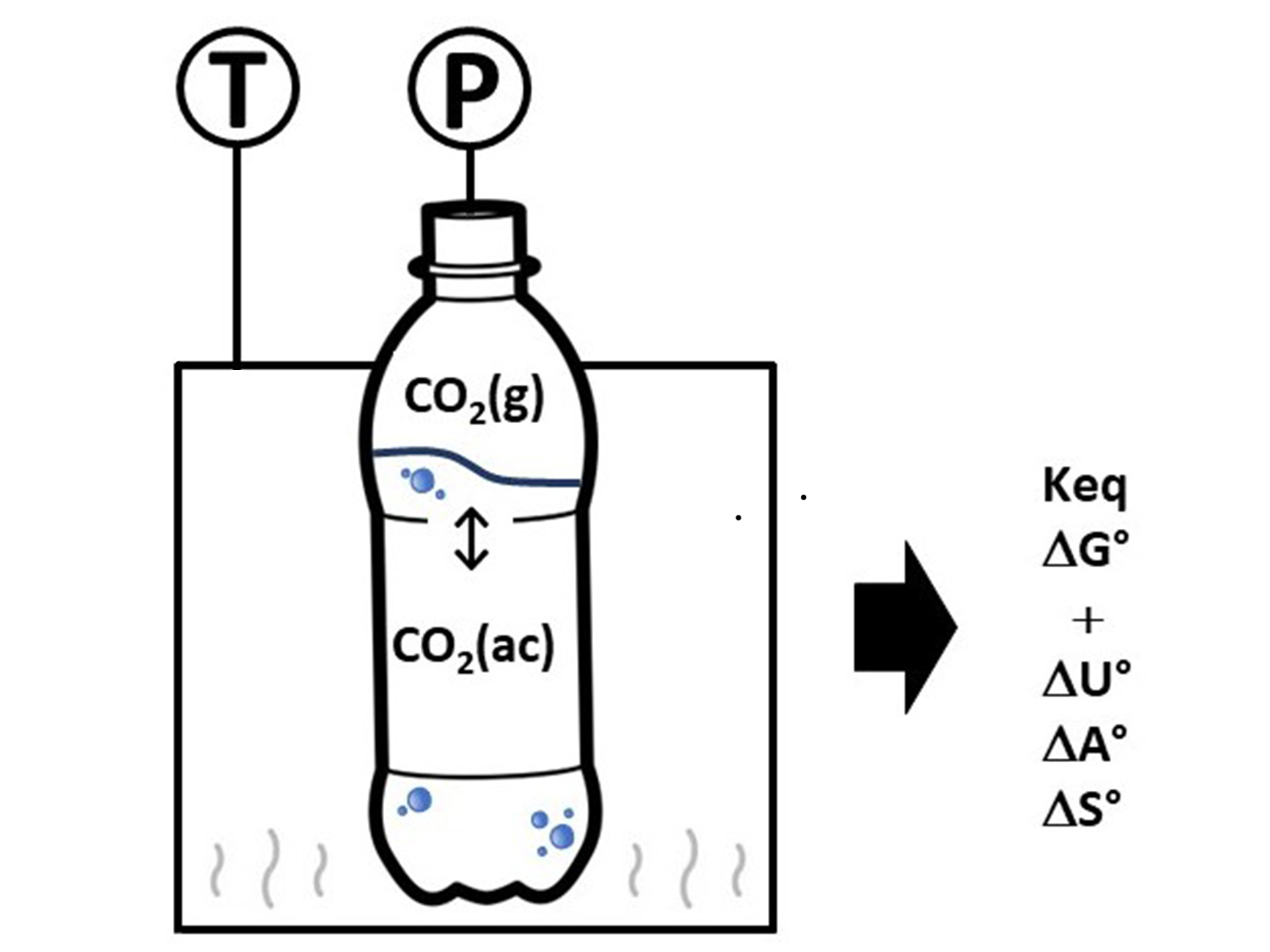
We propose an experiment using a commercial diet cola as a system to determine the Henry´s constant of the chemical equilibrium of carbon dioxide (CO2) between the gaseous and aqueous phases at different temperatures, according to the chemical equation: CO2 (aq) ⇌ CO2 (g).
For this chemical process, the following thermodynamic properties were calculated: ΔH0, ΔS0, ΔG0, ΔU0, and ΔA0 at 298.15 K and the Henry's constant. Using the calculated properties, it is proposed to explain the mathematical relationship between them and their application in the description of the chemical equilibrium of CO2 in the aqueous and gaseous phases of the system. The equilibrium constant was used to explain the variation in CO2 solubility as a function of temperature and pressure. Finally, the solubility of CO2 in the aqueous phase was contextualized with the organoleptic properties of the beverage and the preservation of the shape of the container.
Article Details
Citas en Dimensions Service
References
Atkins, P., De Paula, J. (2010). Physical Chemistry. 9th Ed. H. Freeman and Company. pp. 172, 213, 220.
Baur, J. E.; Baur, M. B.; Franz, D. A. (2006). The Ultrasonic Soda Fountain: A Dramatic Demonstration. J. Chem. Educ. 83, 577-580. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed083p577
Berrio, A. T. (2009). La experimentación dirigida como método eficaz de la investigación y del aprendizaje significativo. [Proyecto aplicado, Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia UNAD]. Repositorio Institucional UNAD.
Chang, R. (2000). Fisicoquímica para las ciencias químicas y biológicas. 3° ed., (R. Zugazagoitia Herranz, Trad.). McGraw Hill. pp. 86-88, 165-171, 215-217, 232-235, 301-315.
Huber C. J. and Massari A. M. (2014). Quantifying the Soda Geyser. J. Chem. Educ. 91 (3), 428-431. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed300694n
Kuntzleman, T. and Sturgis, A. (2020). Effect of temperature in experiments involving carbonated beverages. J. Chem. Educ. 97 (11), 4033-4038. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00844
La química del agua carbonatada. (5 de agosto de 2021) La química del agua carbonatada. QuímicaFacil.net, en la URL https://quimicafacil.net/notas-de-quimica/la-quimica-del-agua-carbonatada/
León Cedeño, F., Jiménez Curiel, C. D. C. (2022). Experiencias docentes durante la pandemia. Curso experimental. Educación Química, 33(2), 82-93.
Levy J. B.; Hornack F. M.; Levy M. A. (1987). Simple Determination of Henry’s Law Constant for Carbon Dioxide. J. Chem. Educ. 64(3), 260-261. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ed064p260
Li D.; Duan Z. (2007). The specification equilibrium coupling with phase equilibrium in the H2O-CO2-NaCl system from 0 to 250°C, from 0 to 1000 bar, and from 0 to 5 molality of NaCl. Chem. Geol. 244, 730-751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.07.023
Miller, J. N.; Miller, J. C. (2005). Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry. (pp.107-111). Pearson.
Nyasulu F.; Barlag R.; McMills L.; Arthasery P. (2019). Mass-based Approach to the Determination of the Henry’s Law Constant for CO2 (g) Using a Diet Carbonated Beverage. J. Chem. Educ. 96(11), 2661-2664. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.9b00082

Educación Química por Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México se distribuye bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivar 4.0 Internacional.
Basada en una obra en http://www.revistas.unam.mx/index.php/req.